Powering the Cosmos & the Earth
The Cosmic Origin & Ubiquity of Hydrogen
Hydrogen was born in the earliest moments of the universe, just minutes after the Big Bang. As the simplest and lightest element—made of just one proton and one electron—hydrogen became the building block of galaxies, stars, and planets. In fact, around 75% of all normal matter in the universe is hydrogen.
In the hearts of stars, hydrogen atoms fuse together under immense pressure to form helium, releasing tremendous amounts of energy. This process, called nuclear fusion, is what makes stars shine. In many ways, hydrogen is the original fuel — from powering stars for billions of years, to being a potential clean fuel for the future, hydrogen is truly the universe's primary fuel source.
Hydrogen in Stellar Processes
In stars, hydrogen serves as the primary fuel through a process known as nuclear fusion. In the intense heat and pressure at a star's core, hydrogen atoms combine to form helium, releasing a tremendous amount of energy in the process. This energy radiates outward, providing the light and heat that support life on planets like Earth. The sun, our closest star, converts approximately 600 million tons of hydrogen into helium every second.
Fusion not only powers stars but also contributes to the synthesis of heavier elements in the universe. As stars evolve, they fuse hydrogen into helium and then into even heavier elements like carbon and oxygen. This stellar alchemy is essential for the diverse array of elements found throughout the cosmos.
Hydrogen's Role on Earth
On our planet, hydrogen is found primarily in water (H2O) and hydrocarbons. Its potential as a clean energy source has garnered significant attention in recent years. When used in fuel cells, hydrogen combines with oxygen to produce electricity, with water vapor being the only byproduct. This makes hydrogen an attractive option for reducing greenhouse gas emissions and combating climate change.
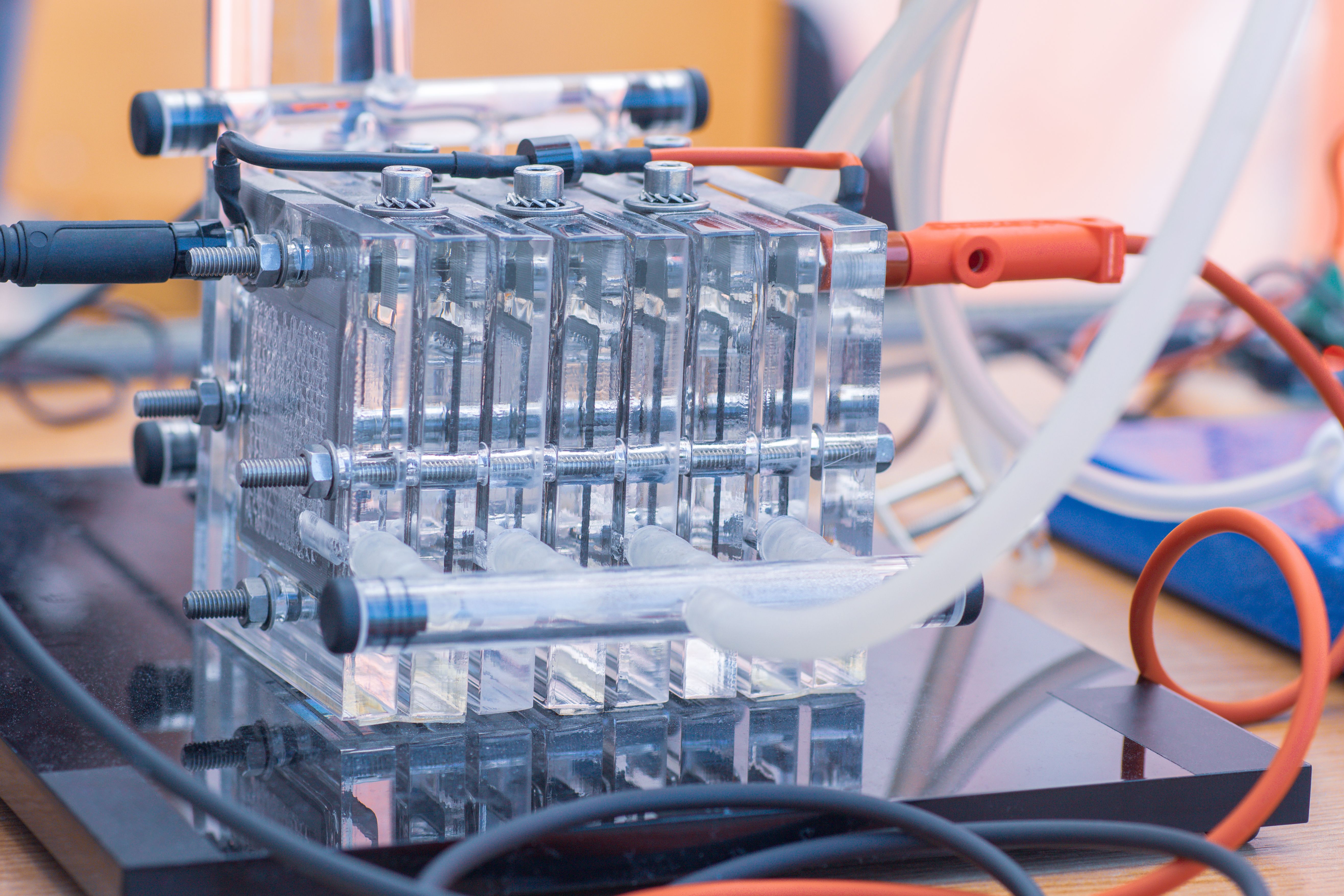
The use of hydrogen as a fuel is not without challenges. Producing hydrogen efficiently and sustainably remains a significant hurdle. Currently, most hydrogen is produced from natural gas through a process called steam methane reforming, which emits carbon dioxide. Researchers are actively exploring greener production methods, such as electrolysis powered by renewable energy sources like solar and wind.
Potential Applications of Hydrogen Energy
The potential applications of hydrogen as an energy source are vast. It can be used to power vehicles, generate electricity, and even store energy from intermittent renewable sources. Hydrogen-powered vehicles are already on the market, offering an alternative to traditional gasoline-powered cars. These vehicles emit only water vapor, making them an environmentally friendly option for transportation.
- Automotive: Hydrogen fuel cell vehicles offer zero-emission travel.
- Industrial: Hydrogen can be used in manufacturing processes that require high temperatures.
- Energy Storage: Hydrogen can store excess renewable energy for later use.
🌍 Global Race for Hydrogen
Countries and corporations are investing heavily in hydrogen as part of their climate goals:
- The EU aims to invest over €470 billion in green hydrogen by 2050.
- Japan launched its Basic Hydrogen Strategy in 2017, leading the way in hydrogen mobility.
- Nigeria, South Africa, and Namibia are exploring green hydrogen for energy exports and economic growth.
“Hydrogen could meet up to 24% of global energy demand by 2050.”
— McKinsey & Company Report for the Hydrogen Council [7]
The Future of Hydrogen
The global push towards sustainability and clean energy is likely to accelerate research and development in hydrogen technologies. Governments and industries worldwide are investing heavily in hydrogen infrastructure, aiming to make it a cornerstone of future energy systems. As technology advances and production methods become more sustainable, hydrogen could play a pivotal role in reducing our reliance on fossil fuels.

Despite its promise, there are still significant obstacles to overcome before hydrogen can become a mainstream energy source. Issues such as infrastructure development, cost reduction, and public acceptance need to be addressed. However, with continued innovation and commitment, hydrogen holds the potential to revolutionize the way we power our world.
✨ Conclusion
Hydrogen is more than just the most abundant element—it is a bridge between the past, present, and future. It fueled the birth of stars, it powers space missions, and it may one day light up our cities without polluting our skies.
As we look to the stars and strive for a cleaner Earth, hydrogen stands as a symbol of what's possible when science, innovation, and sustainability converge. Ultimately, hydrogen's versatility and abundance make it an indispensable component of the universe's energy landscape. As we continue to explore its potential on Earth, we may unlock new possibilities for sustainable living and a cleaner environment.